Neurology
Neurology is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of brain, spinal cord, peripheral nervous system and neuromuscular (muscle-nerve junction) diseases.
Medical Services

Migraine, tension pain, cluster pain and chronic headaches are frequently seen. The patient's complaint history is clinically diagnosed. When the neurologist deems it necessary, imaging methods such as MR or CT can be used for differential diagnosis or initiation of treatment.
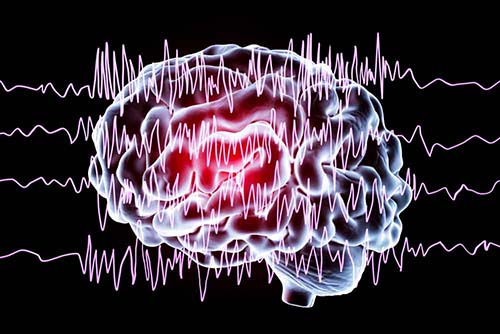
Epilepsy, also known as epilepsy, also known as Sara's Disease, is among the diseases followed by the neurology unit. The most common epilepsy is generalized tonic-clonic seizures. The primary examination methods used in the follow-up and treatment are EEG and MRI. Epilepsy treatment is done by neurologists with antiepileptic drugs.
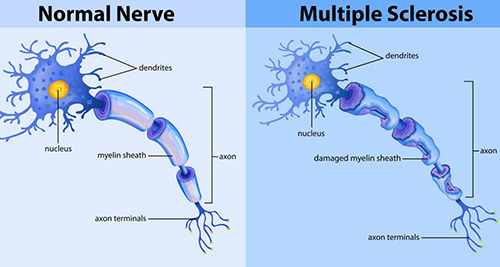
Myelin is a structure that covers the sheath nerve cells, providing their functional integrity. The condition seen due to the loss of this structure due to autoimmunity is Multiple Sclerosis (MS). Diagnosis is made by the presence of contrast material-retaining plaques seen on MRI. Apart from the attack treatment, there are various preventive treatment options that will prevent the patients from having an attack. Apart from MS, other rare demyelinating diseases such as neuromyelitis optica (NMO), Devic's disease are among the diseases in this group.
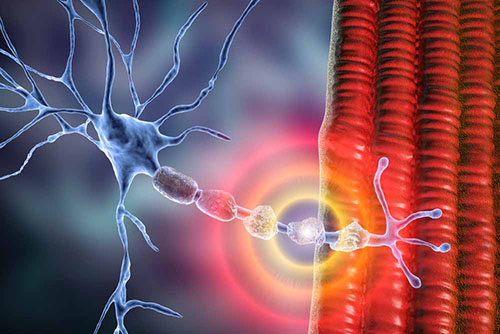
The most common autoimmune disease, Myasthenia Graves affects many muscle groups including eyes, breathing, extremities, swallowing and chewing. With this involvement, drooping of the eyelids, visual disturbances due to weakness in the eye muscles and double vision, difficulty in chewing and swallowing, and weakness in the arm and leg muscles and in the respiratory muscles in the later stages are seen. Apart from the attack treatment, there are various preventive treatment options that will prevent the patients from having an attack.
Another disease that the neurology unit is interested in is Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy, which is a genetically inherited disease.
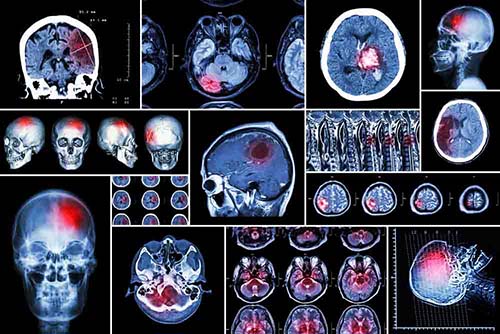
Includes cerebrovascular occlusions and cerebral vascular hemorrhages. Stroke, a cerebrovascular disease, occurs as a result of occlusion of one of the cerebral vessels, cell death occurs in the regions fed by the vessel, and depending on the region, loss of strength, speech loss, dizziness, visual disturbances and loss of consciousness can be seen in the relevant part of the body. In its diagnosis, the occluded vessel and the affected area are detected using MR or CT examinations and treatment is arranged. The follow-up and treatment of brain hemorrhages that do not require surgical evacuation are also performed by the neurology unit. Patients who develop unconsciousness and require respiratory or cardiac support are treated in the intensive care unit, and patients who do not require intensive care support are treated in the clinic.
The most common cause of dementia in the elderly is Alzheimer's disease. It progresses with conditions such as forgetfulness, decrease in cognitive activities, thought disorders, difficulty in doing daily activities, and nutritional deficiency. Apart from Alzheimer's, other diseases and conditions that cause forgetfulness are also followed up and treated by the neurology unit.
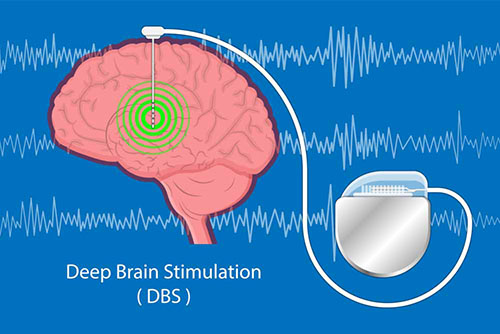
Conditions such as Parkinson's, Tremor, Dystonia, Tic and Cramp are in this group of diseases.
Parkinson's is a disease that occurs with the decrease and damage of the dopamine-secreting cells of the brain in advancing ages, leading to movement disorders and involuntary movements.
Various medical drugs and implantation of a brain pacemaker give very positive results in the treatment.
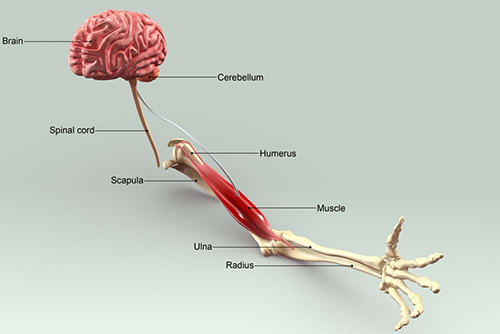
ALS is caused by damage to the motor nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord that allow muscles to move. Muscle weakness begins when impulses are not sent to the muscles through motor neurons. Often there is difficulty in moving the arms and legs, then the whole body. It also becomes difficult to speak, swallow, and breathe. Although there is no definitive cure for the disease today, some symptoms can be treated with early diagnosis and muscle dominance is achieved for a longer period of time. The quality of life of the patient is improved with current treatments.
Diagnosis is made by reflex changes, laboratory tests, biopsy and EMG.
There is currently no specific treatment for ALS. The quality of life of the patients is increased with drug treatments, physical therapy and rehabilitation that allow the patient to continue his daily life comfortably.
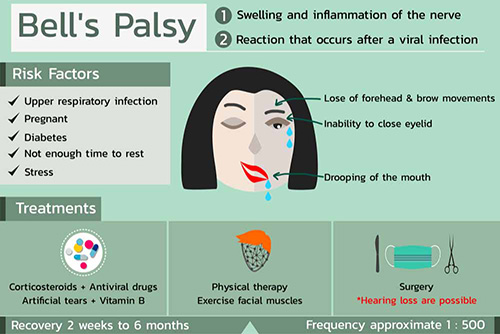
linked to diabetes and other diseases
Such as Meningitis, Encephalitis.

