Cardiovascular Surgery
Diagnosis and surgical treatment of cardiovascular diseases such as vascular occlusions, valve diseases, aneurysms and varicose veins seen in adulthood are performed.
In addition, this qualified branch, which covers newborns, infancy and childhood, and is called pediatric cardiovascular surgery, diagnoses and treats all cardiovascular diseases that require surgery, especially congenital heart diseases, rheumatic heart diseases and rhythm and conduction disorders.
Medical Services
Oxygenation / blood supply / nutrition of the heart is not with the blood in the heart itself; It is fed by the right and left heart arteries (coronary arteries) separated from the aorta.
With the development of a condition called atherosclerosis, plaques form inside the vessel. When these vessels or their small branches are clogged, a picture called heart attack (myocardial infarction) occurs as a result of destruction in the relevant area they feed. This situation can be dangerous most of the time, causing heart contraction defects and fatal arrhythmias.
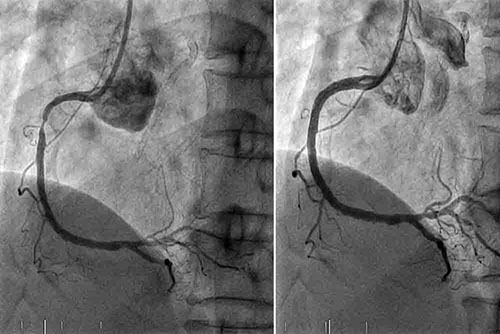
Coronary artery disease is usually diagnosed by clinical complaints such as chest pain that occurs with exercise and improves with rest, a complaint of great pain starting on the chest and hitting the inner left arm, or detection of ischemia findings on ECG or scintigraphy during stress test, or significant narrowing or occlusion of the coronary arteries in coronary angiography.
With positron emission tomography (PET), it can be checked whether the heart muscle is alive and whether the incoming blood is sufficient.
In coronary angiography, a thin small bendable catheter is placed in one of the great arteries of the arm or leg and advanced to the aorta, where the coronary arteries originate. A dyed substance is delivered from the catheter to the coronaries. In the meantime, it is determined how much narrowing in which parts of your coronary vessels is on the film.
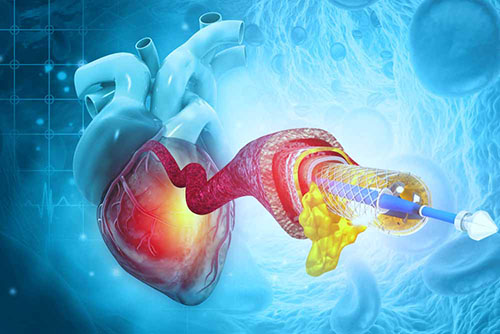
The stent is a method that can be preferred in a patient who is having a heart attack or in patients with a single artery in the heart.
Like coronary angiography, a catheter is inserted through the arm or inguinal vein, and a stent is placed in the stenosis in the veins to open the veins. Depending on the stenosis of the vessel and other risk factors, a drug-free or medicated stent can be used. The most serious problem with stents today is the possibility of re-occlusion. For this, it is necessary to use blood-thinning (anticoagulant) drugs for life in patients who have stents.
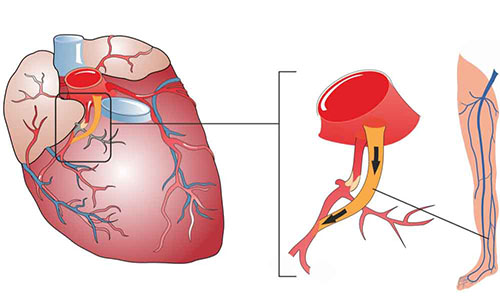
Bypass is the preferred treatment method especially in multiple vascular occlusions.
Bypass surgery is the process of attaching the veins from the legs or the artery from the chest or arm to the clogged coronary artery of the heart. After this intervention, the blood flow that cannot pass through the occluded vein passes through the newly inserted veins and feeds the heart.
This operation often requires an open-heart surgery; in which, the human heart and lungs are completely stopped, in order to work more freely on the heart. Meanwhile, the blood and oxygen need of the brain and other organs are met by an artificial 'heart-lung' machine located outside the body.
It is a less invasive surgical technique compared to open bypass surgery. The incision site is smaller, the anterior chest wall bone is not removed, and the procedure can be performed while the heart is operating. This reduces the risk of complications and the recovery time of the patient. It is usually applied in stenosis in the anterior descending branch of the heart.
Robot-assisted coronary bypass surgery is not suitable for every patient. It is used to bypass the LAD vein in the anterior aspect of the heart.
In addition, endoscopic vein removal method can be used to remove veins from the leg and arm.
Although it varies according to the number of vascular bypasses performed in all types of surgery, they are surgeries that last between 2 and 4 hours on average.
Since the first 24 hours are the period when bleeding and rhythm disorders are most common, patients are followed up in the intensive care unit for approximately 24 hours after bypass surgeries.
After the surgery, patients usually stay in the intensive care unit for one or two days and are taken to the ward the next day. During these days in the ward, the patient will be able to meet his own needs. Patients are discharged home on the 4th or 5th day, in case they do not face any problems.

The mitral valve area, which is normally 4-6 cm2, gradually narrows and becomes smaller due to streptococcal infections in childhood. The complaints of the patient begins if the lid area falls below 2 cm2.
With mitral valve stenosis, the left atrium enlarges and its pressure increases. This situation increases the pulmonary vein pressure with the accumulation of fluid in the lung. If left untreated, the right side of the heart is also affected by this condition, and after a while, the right heart cavities expand and tricuspid valve insufficiency occurs.
As the left atrium enlarges, it causes irregular heart rhythms such as atrial fibrillation, which can be fatal.
Mitral valve stenosis is diagnosed mainly by echocardiography.
The follow-up and treatment of all valve diseases are determined according to the effort capacity. According to the New York Heart Association's (NYHA) Functional Classification, surgery is required in case of complaints during heavy activity with heart rhythm disorder, or in case of complaints during daily simple activity or resting alone.
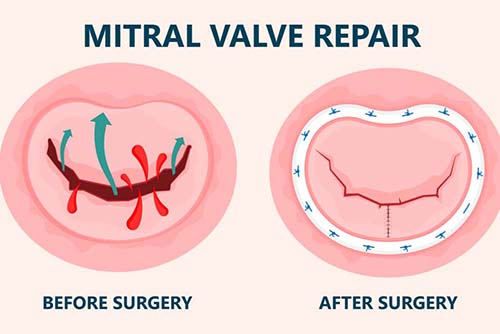
Mitral valve regurgitation is when the left ventricle contracts, and some of the blood that needed to be pumped to the body return back to the left atrium due to leakage in the valve. As a result, over time, the heart begins to grow, the pressure in the lungs increases and complaints begin to occur.
Patients with complaints, deterioration in cardiac functions or developing heart enlargement should be operated on without delay.
The most commonly used method in mitral valve surgeries; is the classical open heart surgery. In addition, methods such as Minimally Invasive and Robotic Surgery are used.
Repair of the mitral valve is the primary choice. If this method is not considered by your doctor to have satisfactory results, the mitral valve is replaced with a suitable prosthetic valve. If a mechanical valve is preferred as a prosthetic valve, it will last for many years as long as it is not infected. In the use of mechanical valves, it is necessary to use blood thinners for life. In biological valves, it is not necessary to use blood thinners after the first 3 months.
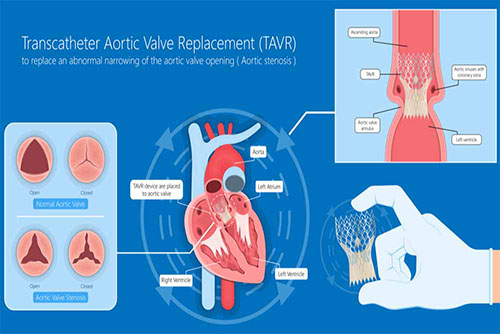
The aortic valve opens when the heart contracts and allows it to pump blood throughout the body. When the heart muscle relaxes, the aortic valve closes, preventing the return of blood pumped by the heart to the body.
There are two functional disorders of the aortic valve. These are aortic stenosis and aortic regurgitation.
Aortic Valve Stenosis and Aortic Insufficiency
In aortic stenosis, the heart cannot easily pump blood to our body. The heart has to work harder, which over time weakens the heart and causes heart failure. When the aortic valve area, which is normally 3-4 cm2, falls below 1 cm2, severe aortic stenosis occurs. This is a serious and fatal condition.
The definitive diagnosis of aortic stenosis is made by echocardiography.
Aortic regurgitation is when the aortic valve relaxes, blood flows back to the heart.
The definitive diagnosis of aortic regurgitation is made by echocardiography, as in aortic stenosis.
Bicuspid Aortic Valve
Congenital aortic valve with 2 leaflets instead of 3. It is the most common congenital heart anomaly known to be inherited. Aortic stenosis, aortic regurgitation, aortic aneurysm (bubbling) and related aortic dissection may be seen in patients with bicuspid aortic valve. Therefore, close follow-up of these patients is important.
Surgical interventions for bicuspid aortic valve and aortic prosthetic valve types are the same as for normal aortic valve interventions.
When and how is surgery performed in Aortic Valve Diseases?
Surgery is required if the contraction strength of the heart has decreased below 50%, if there is a decrease in performance during exercise or if the disease progresses rapidly. Repair of the aortic valve is the primary choice. Aortic valve surgeries are performed in the form of standard open-heart surgery. There are also centers that do it with the Minimally Invasive method.
The advantages and disadvantages of prosthetic valve use have the same characteristics as valve replacement in mitral valve regurgitation.
Another aortic valve surgery method that has become popular in recent years is the OZAKİ procedure.
Prosthetic valves are not used in Ozaki surgery. Instead, the calcified valve is cleaned and a patient-specific valve is created using its own pericardium.
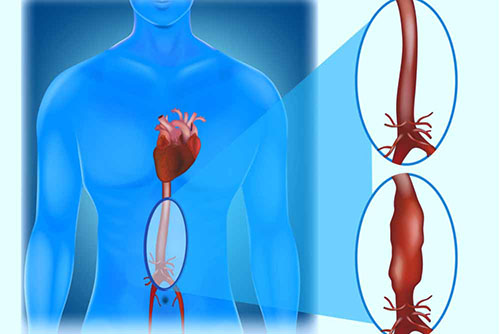
The aortic vessel diameter is larger than normal. This disease, which we call aneurysm, turns into aortic dissection, known as rupture of the aortic vessel, over time.
If the aneurysm is in the thoracic cavity, it is called a thoracic aneurysm, and if it is in the abdominal cavity, it is called an abdominal aortic aneurysm.
Aortic aneurysm can be detected by examination, x-ray, computed tomography and MRI.
If the aneurysm diameter exceeds 55 mm, if the aneurysm has enlarged >5 mm or more in the last 6 months regardless of its diameter, surgery should be performed.
In the part of the aortic aneurysm emerging from the heart, these operations are usually performed with open surgery or minimally invasive techniques.
TEVAR (thoracic endovascular aortic repair) technique is used in thoracic aortic aneurysm surger.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm surgery, on the other hand, is usually performed with a catheter-based inguinal EVAR (abdominal endovascular aortic repair) procedure.