Neurosurgery
It is the branch of science that examines and treats diseases of the brain, spinal cord and the skull bones, which are the bone structures that protect them, and the spine.
The disease that concerns the neurosurgery clinic can be grouped under two main headings. These are cranial (brain) diseases and spinal (spine-spinal cord) diseases.
Medical Services
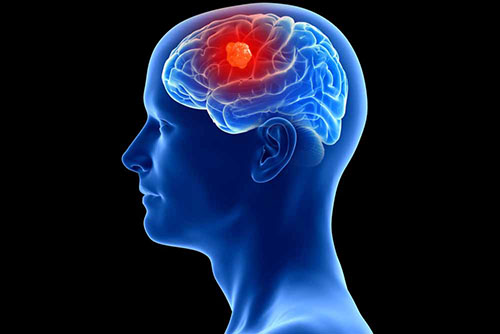
These diseases can be seen at any stage of life. They can be benign (benign) or malignant (malignant) depending on the nature of the tissue in which the tumor occurs.
Glial tumors originating from the brain's own tissue are malignant tumors that are frequently seen in adulthood. In the treatment, surgery and then radiotherapy and chemotherapy protocols can be applied. One of the most important parameters affecting survival is the effectiveness of surgery. This is closely related to surgical experience and clinical competence. Tumors originating from the membranes of the brain are generally benign and a complete cure is provided with an effective surgery.
Although there are many parameters that affect the prognosis (course) of the patient in metastatic (spread elsewhere) tumors, the prognosis is generally poor since another cancer spreads and tumor masses form in more than one place in the brain.
In brain tumors, it is very important in the region where it occurs as much as the tissue of the tumor. For example, the surgery of a superficial tumor can be performed more smoothly, while the surgery of a deeply located tumor and/or close to an important center in the brain may be more complicated. E.g; After the surgery of a tumor close to the motor area, the probability of waking up as paralyzed is higher than in other localized tumors.
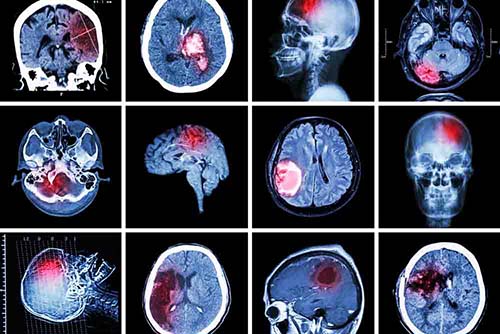
Bleeding to different parts of the brain due to the damage to brain vessels. Vascular damage may develop due to trauma, as well as vessel rupture due to uncontrolled hypertension or rupture of an aneurysm (bubble).
The area where the bleeding occurs and the size of the bleeding are important parameters in the damage to the brain at the time of the first bleeding.
For example, epidural hemorrhage between the uppermost membrane of the brain and the skull bone can be fatal by causing serious compression, and evacuation of the hematoma (blood mass) with early surgical intervention would be life-saving.
Even if subarachnoid hemorrhage due to bleeding from an aneurysm (bubble) is not fatal at first, it must be treated with surgical or interventional methods because of the risk of a second hemorrhage.
It should also be kept in mind that bleeding can progress with serious complications in elderly patients who use blood thinners and have hypertension.
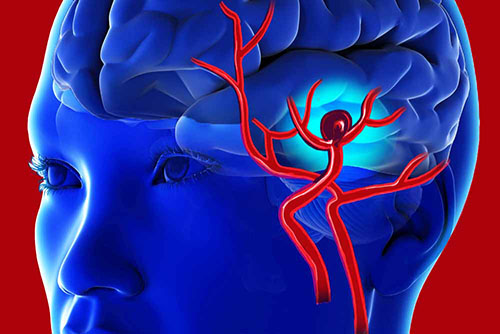
It includes vascular anomalies in the brain that are congenital or occur as a result of environmental factors in life. The most common vascular anomalies are aneurysm (bubble), arteriovenous malformations and cavernomas. Unless there is bleeding from a vascular anomaly, these diseases are very rare to cause symptoms. When they bleed, they can have fatal consequences. Therefore, when a cerebrovascular disease is encountered –especially in an asymptomatic vascular disease- it is very important to decide when surgery or other treatments should be applied. It should be kept in mind that non-surgical methods can also be applied in these diseases. E.g; Today, interventional coiling and stenting procedures are as important as open surgical clipping in the treatment of aneurysms.
Again, gamma-knife radiotherapy can be used quite effectively in the treatment of arteriovenous malformations. The important thing is to decide in the most accurate way which procedure will be applied in which patient.
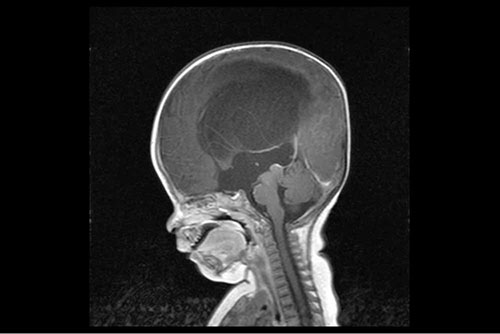
It can be roughly defined as a collection of water in the brain. There are 4 spaces in the brain called ventricles, in which the cerebrospinal fluid circulates. It is a disease characterized by the accumulation of more than normal amount of fluid in these cavities, usually due to an obstruction and/or malabsorption in the ventricular system.
In cases of chronic hydrocephalus, ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery can be performed after symptoms such as gait disturbances, urinary incontinence, and slowing of mental functions are observed. The purpose of this shunt system is to drain the fluid in the ventricular system into the abdominal cavity with the help of a catheter. In this way, the ventricles will become smaller and the pressure on the brain tissue will decrease.
Acute (sudden) hydrocephalus, on the other hand, creates a clinical picture that can result in death as it will suddenly create a high pressure on the brain tissue. In this case, rather than shunting, the fluid is discharged with a system called external ventricular drainage.
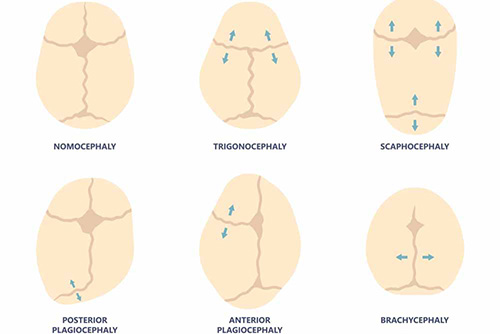
In the mother's womb, the skull bones are separate from each other and combine in the postnatal period and serve as a single bone. The places where the bones meet are called sutures. The brain will not be able to develop if it merges with this bone sooner than expected and the sutures are closed. This will hinder mental and motor development. The group of diseases that make up this clinical picture is called synostoses. In this case, the skull bones of the child are separated from each other by surgical intervention and the normal development of the brain is ensured.
Although it is known as cerebellum prolapse among the people, they are posterior fossa (posterior pit of the skull) anomalies that can contain many components apart from prolapse of the cerebellum into the spinal canal. They reveal findings characterized by compression of the posterior cavity structures and are treated with decompression (elimination of pressure) applied to this area. Since hydrocephalus may accompany some of them, treatment can be applied for it.
Just like herniated disc, the herniated soft tissue material compresses the nerve roots that come out of the neck and go to the arms. In the clinic, numbness, pain and numbness can be seen in the arms and fingers. In its treatment, physical therapy and rehabilitation, interventional pain treatments and surgical treatment are applied. In surgical treatment, after the hernia material is removed, a cage is placed between the two vertebrae.

It is a disease that develops as a result of herniation of soft tissue materials called intervertebral disc, located between the vertebrae that make up the spine, and compression on the spinal cord and nerve roots. Symptoms related to the affected nerve root occur. Depending on the level of pressure and the amount of pressure, pain, numbness, numbness, urinary and stool incontinence, numbness in and around the genitals, paralysis in the muscles stimulated by the nerve can be observed.
Treatment is given according to the patient's complaints, neurological examination and radiological imaging. In treatment, physical therapy and rehabilitation, interventional pain treatments and surgical intervention can be applied. Which treatment will be applied to which patient is decided after the examination of an experienced physician. In the surgical treatment, the compressive hernia material is removed and the spinal cord and nerve roots are relieved.
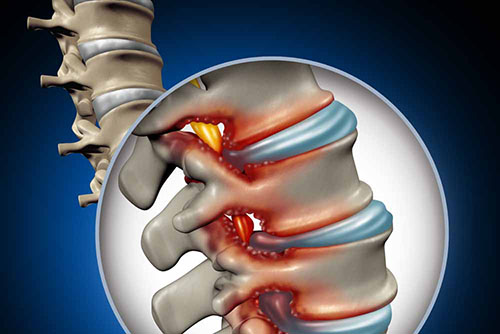
It is the clinical picture that occurs as a result of the spinal canal narrowing over time and compressing the spinal cord passing through it. The symptoms are especially caused by the blood supply disorder caused by the pressure on the spinal cord. Pain that increases with walking and the desire to sit and rest are important findings in these patients. Surgical techniques, interventional pain treatments, physical therapy and rehabilitation can be applied in its treatment. In surgical treatment, the spinal cord is relieved by opening the posterior column of the spine. Thus, the blood flow returns to normal and the patient's complaints are relieved.
Developmentally, it is a lower unit ending in the spinal cord where it should have a nervous ending. As childhood develops, as the child grows in height, the spinal cord will be stretched. This will not lead to straying, function and digestive disorders. You can start with this allowance. To continue without surgical intervention in asymptomatic cases with eyes in adult age.
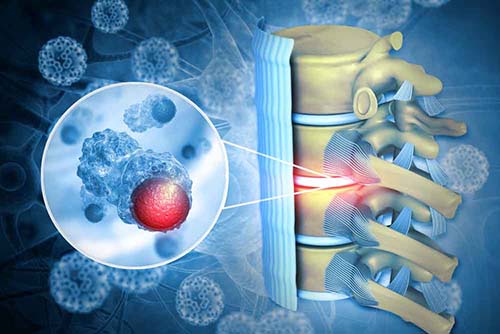
Tumors that occur as a result of the spread of cancer from the spinal cord tissue, membranes or elsewhere. Clinically, it is closely related to the size of the tumor and the pressure it puts on the spinal cord. In addition, pain is an important finding in tumors involving only bone tissue. Surgery has an important place in the treatment. In some cases it is important to stabilize the spine with instrument systems after surgery.

It covers damage to the bone structure of the spine after a high-energy trauma. If a fracture in the spine is compressing the spinal canal, the spine should be stabilized with instrumentation systems by decompression. In collapsed fractures that do not cause compression into the spinal canal, surgery can be performed by inflating the broken vertebra with a balloon and injecting bone cement into it. This surgical intervention, known as kyphoplasty, not only significantly reduces the patient's pain, but also prevents complications related to collapse that may occur in the future. Only bone cement can be given without inflating it with a balloon in patients with low collapse.

