Pediatric Surgery

In the Department of Pediatric Surgery; Diagnosis and treatment services are provided for pediatric patients. The section covers the operations of pediatric patients under the age of 18.
Medical Services
It is the process of surgically cutting the tissue called preputium covering the glans penis in a certain shape and length and exposing the glans penis. It is performed due to skin adhesions that do not respond to treatment, recurrent urinary tract infections, urinary reflux, voiding disorder, penile head infection or religious-sociocultural reasons.
It is one of the most common operations in pediatric surgery. Swelling in the groin area is usually the first finding. It is more common in premature children. Swelling increases in situations that increase intra-abdominal pressure such as straining, crying, coughing. The definitive treatment is surgery. The duration of the operation is between 30-90 minutes. The success rate of the surgery is 99%.

Umbilical hernia in children occurs as a result of the umbilical canal not closing completely after birth.
There is temporary swelling in the belly with crying and straining. It disappears on its own when the baby relaxes. If necessary, definitive diagnosis is made by ultrasonography.
Babies with umbilical hernia do not need any treatment within the first two years of age.
It should be corrected surgically if it has not passed in 3 years in girls and 4 years in boys, If suffocation has occurred even once, and if the diameter is 1.5-2 cm or more. After surgical treatment, the hernia sac is found and excised with a half-moon incision made under the umbilicus under general anesthesia, the fascia tissue is closed with absorbable sutures.
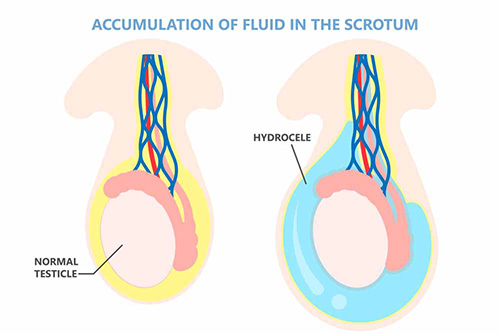
Sometimes the organs do not descend into the sacs (scrotum) if the inguinal canal is not closed. However, the fluid in the abdomen descends into the sac. In this case, the sac swell and these fluid-filled sacs are called hydroceles. If the front and back of the hydrocele sac is closed with a membrane and closed to the inlet of fluid, a palpable mass is present. This mass is called a cord cyst. If the hydrocele does not heal after 1 year of age, it requires an operation.
As babies complete their development in the womb, the tissues that will turn into testicles in the future appear just below their kidneys. As the baby develops, the testicles move from the inguinal canal to the scrotum. Shortly before birth, both testicles settle in the sac. The reason why the testicles formed first in the abdomen and then descend into the sac is that they can perform their functions in an environment at a lower temperature than the body temperature.
The inability of one or both testicles to complete this descent, in other words, to place them in the sac, is called undescended testis. After six months, the possibility of spontaneous descent of the testicles into the sac is almost nonexistent. A specialist should be consulted to plan the treatment without losing any time.
Congenital muscular torticollis is a name given to the appearance in the neck that occurs at birth or soon after, in which the head is prone to one shoulder. It is a congenital disease that occurs most commonly in the neck muscles called sternocleidomastoid and is manifested by thickening and shortening of the muscles. A non-tender hard mass in the muscle on the side of the neck may be palpable in a child.
This operation will be performed under general anesthesia and by a pediatric surgeon in the operating room. An incision of approximately 4-5 cm is made on the right side of the neck. The sternocleidomastoid muscle and deep neck fascia (membranes) causing tension are cut.
- Conditions of Bleeding from the Anus
- Intestinal Knotting (Invagination)
- Rectal Polyp (Juvenile Polyp)
- Anus Fissure (Anal Fissure)
- Constipation and Incontinence in Children
- Hirschsprung's Disease
- Stomach Outlet Obstruction of Babies (Infantile Pyloric Stenosis)
Tumor is a result of the proliferation of cells and extra mass formed by tissue growth in any tissue in the body.
Pediatric oncological situations represent a group of diseases, which together with the proliferation of abnormal cells in any tissue, metastasize to another part of the body with blood or lymphatic flow and impair body health. 30% of childhood cancers are leukemias and the remaining 70% are solid cancers (cancers from organs and various tissues). The second most central program in children is the nervous system probabilities (brain tumors). Next comes Lymphoma, Neuroblastoma and Wilms tumor. Lymphoma is divided into two as Hodking lymphoma, which is a gland tumor that can start most commonly in the neck glands, lymph nodes, and rarely in organs such as the liver, spleen, and skin; and Non-Hodking lymphoma, which is a disease characterized by uncontrolled proliferation of lymphocyte series cells.
Neuroblastoma arises from nerve node cells. Wilms tumor, also known as nephroblastoma, is the most common type of malignant kidney tumor in children. Osteosarcoma and Ewing sarcoma are the most common bone tumors in childhood. Childhood cancers can be treated such as surgery, chemotherapy and radiotherapy, and 70% of these can now be cured with full cure.

It includes the surgical treatment of functional and anatomical disorders in organs and limbs that occur as a developmental defect in the womb of children.

