Robotic Surgery in Turkey Costs, Advantages and Procedure
- History of robot-assisted surgery
- How does the DaVinci system work
- What are the advantages of robotic-assisted surgery?
- Today's standard in Robotic Surgery
- Robot Assisted Surgeries in Turkey
Robotic surgery is a further development and technical improvement of laparoscopic surgery. The minimally invasive technique is supplemented with a 3D camera system and ergonomically controllable instruments with advanced mobility comparable to that of the human hand. This allows minimally invasive operations to be carried out with the highest precision and tissue protection.
History of robot-assisted surgery
In the 1980s, surgical robots were developed for the American military with the aim of treating injured soldiers at the front with remote-controlled telerobots. In 1995, the company Intuitive Surgical ® was created for the development of prototypes for civil use. In 1999 the first DaVinci® system for robot-assisted laparoscopic surgery was presented. The first robot-assisted removal of a prostate was performed in Frankfurt in 2001. Today, this operation is one of the standard interventions in robotic surgery.The Da Vinci system is not an actual robot as it cannot perform the operation itself. Accordingly, we speak of a robot-assisted system that transmits the movements of the surgeon to the instruments precisely and without shaking. The surgical experience of the surgeon also plays an important role in robot-assisted surgery .
How does the DaVinci system work
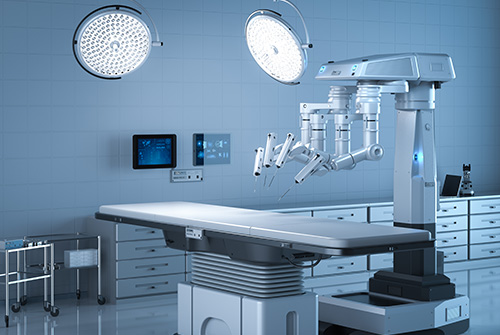
The Da Vinci system consists of a patient trolley (“robot”), a system trolley and a console. The patient trolley has four movable arms and is placed on the operating table above the patient for the procedure. One arm is used to control the 3D camera. Various instruments can be docked to the other three arms.As in conventional laparoscopic surgery, 5-12mm introducer sleeves (trocars) are used, which are inserted through the patient's abdominal wall. The abdominal cavity is first filled with CO 2 gas. The specially developed robotic instruments are introduced through the trocars, which are moved with the help of the robotic arms.
The operator moves the robotic arms and thus controls the instruments from the console. With the help of special hand straps, the movements can be carried out intuitively and precisely. The surgeon looks into the console's binoculars (similar to normal binoculars), where he can follow his movements in real time in a high-resolution three-dimensional image. The pedals located at the bottom of the console can be used to obliterate small blood vessels using high-frequency current. In addition, the surgeon can use it to switch between individual instruments and control the camera precisely as required.
While the surgeon sits at the console, the assistant supports him at the operating table. He is responsible for changing the instruments and inserting the required materials (e.g. suture material) into the abdomen via an additional trocar.
What are the advantages of robotic-assisted surgery?
As with conventional laparoscopic surgery, the patient benefits from less pain in the absence of a large abdominal incision, from a shorter recovery time and from better cosmetic results. Clinical studies have even shown that blood loss can be even lower with robot-assisted technology. What has not yet been proven in studies but is clear that the patient also benefits from the advantages of the system.
The surgeon experienced in laparoscopic surgery learns the robot-assisted technology very quickly thanks to the intuitive handling of the system. The excellent 3D overview with up to 10x magnification enables more precise work. The surgeon can work in an ergonomic position on the console and benefits from the freedom of movement of the instruments with a total of seven degrees of freedom and up to 5x gear reduction. The physiological movements of the human hand can thus be transferred directly to the instrument, which further increases precision.
The computing unit (computer) positioned on the system trolley can filter out not only different translations but also natural shaking movements, which makes instrument control highly precise and intuitive. Even complex movements such as suturing and knotting a thread are easier to perform than in laparoscopic surgery. The resident can follow the operation live on the monitor mounted on the system trolley.
Today's standard in Robotic Surgery
As already mentioned, radical prostatectomy for prostate carcinoma has become established in robot-assisted technology in urology. Further interventions on the kidneys, the renal pelvis system and the adrenal glands are regularly carried out by experienced urologists.The Da Vinci prostatectomy has been established for over 10 years and has achieved a high degree of standardization. Studies have shown significant advantages in the perioperative course. The oncological results are comparable to open surgery. In addition, certain advantages could be recorded in the functional results, for example in terms of potency or continence.
Robot Assisted Surgeries in Turkey
On Innovacare hopitals, the following general and visceral surgery procedures are performed using the Da Vinci system.
- Inguinal Hernias : In this operation performed with the Da Vinci System, the learning curve is very short. The initially extended operation times are soon reduced to the values that are familiar from laparoscopy. A bilateral inguinal hernia can be performed in less than an hour. In addition, there are the installation times, which minimally increase the operating time. The overview and the ergonomics for the surgeon contribute to better results and clear advantages for the patient as well.
- Abdominal wall and incisional hernias : Here the Da Vinci system makes it possible to perform an operation that otherwise had to be performed openly. With the help of the robot, a plastic mesh can be implanted from the inside into the abdominal wall, which is not possible with conventional laparoscopic technology. After this operation, the patients definitely have fewer symptoms and can be discharged from the hospital after a short time. The complication rate is extremely low.
- Fundoplication : The repair of a diaphragmatic hernia is usually performed laparoscopically. A relatively large amount of stitching is required for this operation, which can be carried out much more easily and quickly with the Da Vinci system. The three-dimensional view in robot-assisted surgery also brings evident advantages here.
- Rectopexy : The laparoscopic treatment of obstructive defecation disorders resp. rectal prolapse is a complex operation that also requires a lot of stitches. Accordingly, the Da Vinci system also has improved options here, which are to the benefit of the patient.
Robotic Surgery for Heart
The only method of cardiac surgery available in the past was open surgery. A lengthy chest incision is necessary for open heart surgery. In order to see and operate on the heart, surgeons must also cut the sternum and expose the rib cage. Although open heart operations are still done, there are now minimally invasive techniques that doctors may use.Thoracoscopic surgery and robot-assisted da Vinci surgery are two minimally invasive surgical methods for coronary artery bypass surgery. To introduce surgical tools and a camera for imaging, physicians just need to make a few tiny incisions. When performing thoracoscopic heart surgery, surgeons use special devices and monitor the magnified images from the screen.
Mitral valve repair may also be performed by thoracoscopy or robot assistance. Mitral valve repair with a catheter is a third less invasive choice. A tiny cut is made in the groin, and a thin tube (catheter) is then inserted into a vein to reach the heart. The valve will be fixed or changed by surgeons.
Heart operations that involve robotic surgery include:
- Fixing the mitral valve
- Septal Myemectomy
- Repairing a tricuspid valve (with mitral valve repair)
- Repair of the atrial septal defect (ASD)
- Repair of the patent foramen ovale (PFO)
- Removal of tumors located in heart
Robotic Surgeries in Urology
Robotic surgery is utilized in urology to treat a number of illnesses, including prostate, bladder, and kidney malignancies as well as other non-cancerous problems of these organs.The most popular urological robotic surgical techniques are:
- Prostatectomy (removal of the prostate)
- Nephrectomy, both partial and radical (removal of the entire kidney)
- Pyelo/ureteroplasty (removal and reconstruction of part of the urinary tract)
- Cystectomy (removal of part or all of the bladder)
- Dissection of the retroperitoneal lymph nodes (removal of lymph nodes behind the abdomen)
- Implantation of ureters (treatment of the tubes connecting the bladder to the kidneys)
Robotic Gynecological Surgery
One of the most recent developments in less invasive surgical methods is gynecological robotic surgery. Our gynecology doctors can treat a range of disorders affecting a woman's reproductive systems by using a small, lighted binocular and tiny equipment managed by a robotic system.
Conditions That Gynecological Robotic Surgery Can Treat
Our skilled gynecological surgeons use gynecological robotic surgery to treat diseases like:
• Discomfort and heavy bleeding
• Pelvic organ prolapse
• Endometriosis
• Gynecological malignancies such as cervical, ovarian, and uterine cancer
• Abdominal and pelvic pain
• Uterine fibroids
Robotic Surgeries in Gynecology
Robotic endometriosis resection is a gynecological robotic surgery procedure that removes abnormal growths in the pelvic area without harming the uterus or other internal organs.
Robotic procedures to remove the uterus robotic hysterectomy
Robotic myomectomy for removal of myomas
Robotic sacrocolpopexy for repairing pelvic organ prolapse using a surgical mesh to keep the organs in place.
Robotic Procedures for Colorectal Surgery
- Colon resection
- Rectal resection
- Rectopexy or surgery for a prolapsed colon.
Robotic Thoracic Surgery
Robotic thoracic surgery is a form of minimally invasive thoracic surgery that is used in some lung cancers. It can be used to remove damaged lung tissue and adjacent lymph nodes in some cases. It is also known as robotic-assisted thoracic surgery. In robotic surgery, the surgeon will operate the robot's tools while seated at a console adjacent to the patient in the operating room. To observe the interior of the chest cavity, a tiny 3D high-definition camera is first introduced into one of the incisions. Then, tiny incisions are created between the ribs to implant robotic devices. The doctor's hands at the console have total control over robotic devices. Through one of the incisions, the surgeon extracts lung tissue. The surgeon can remove lung tissue thanks to the equipment and enlarged perspective, which eliminates the need for bigger cuts to expose the chest or spread the ribs. Lung cancer surgery, as well as other chest treatments involving the lungs, esophagus, thymus, and some cardiac procedures, can be performed with the robotic approach.Robotic chest surgery procedures include thymectomy, mediastinal mass resection, and lung cancer surgery (removal of the thymus gland).

Future of Robotic Surgery
The costs of robot-assisted surgery are currently relatively high. Both the acquisition and the maintenance and purchase of the special instruments are not cheap. In the future, cheaper and better robots will be developed, which can offer the surgeon even more options. Robotic surgery is unstoppable. The future has already started.There are no comments yet. Would you like to add a comment?
In accordance with Article 10 of the Personal Data Protection Law (PDPL,KVKK) titled Data Controller's Obligation to Disclose, we use cookies in accordance with the legislation, limited to the purposes specified in the privacy policy.

