IVF Treatment in Turkey Costs and Procedure
- IVF Treatment in Turkey
- Reasons for IVF Treatment
- Risks of IVF Treatment
- Preparation Before IVF Treatment in Turkey
- How IVF is Done Step by Step
- After IVF Treatment
- Results of IVF Treatment
- IVF Treatment Costs in Turkey
IVF Treatment in Turkey
The IVF treatment, also called in vitro fertilization, is a complex set of procedures to aid fertility or prevent genetic problems and make it easier to have a child.
During IVF treatment, mature eggs are collected from the ovaries and fertilized by sperm in a laboratory. The fertilized egg (embryo) or eggs are then transferred to the mother's womb. This cycle of IVF treatment takes about three weeks. Sometimes, different approaches can be added to the IVF treatment steps mentioned, and as a result, the process may take longer.
IVF treatment is the most effective form of assisted reproductive technology. The IVF procedure can be done using the person's own eggs and the sperm of his partner. However, IVF treatment can also be performed using eggs, sperm or embryos from a known or anonymous donor. In some cases, the embryo created with IVF treatment can also be transferred to a surrogate mother.
Your chances of having a healthy baby after IVF treatment depend on many factors, such as your age and the cause of your infertility. In vitro fertilization is an invasive method that takes time. If more than one embryo is transferred to your uterus, IVF treatment can produce a pregnancy with more than one fetus (multiple pregnancy).
Your doctor will share the details of the IVF treatment with you to help you understand how the IVF procedure works, the potential risks, and whether this infertility treatment method is right for you.
Reasons for IVF Treatment
In vitro fertilization (IVF) is a treatment option for infertility or the treatment of possible genetic problems in the baby. If IVF is done to treat infertility, you and your partner can try less invasive treatment options before trying IVF, including fertility drugs or intrauterine insemination to increase egg production – a procedure in which ovulation-time sperm is placed directly near your womb.

In some cases, IVF treatment is offered as the primary treatment for infertility in women over 40. The presence of various health problems may also be the reason for IVF treatment. IVF may be a good option for treatment if you or your partner have any of the following:
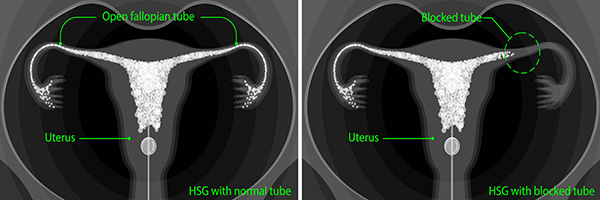
- Fallopian tube damage or blockage: Fallopian tube damage or obstruction makes it difficult for an egg to fertilize or for an embryo to reach the uterus.
- Ovulation disorders: If ovulation occurs infrequently or not at all, there is less chance of fertilization as there will be fewer eggs available for fertilization.
- Endometriosis: Endometriosis occurs when uterine tissue grows outside of the uterus, often affecting the function of the ovaries, uterus, and fallopian tubes.
- Uterine fibroids: Fibroids are benign tumors in the wall of the uterus and are common in women in their 30s and 40s. Fibroids can prevent the implantation of the fertilized egg.
- Previous tubal removal or tubal ligation surgeries: If you have undergone tubal ligation, a type of procedure in which your fallopian tubes are cut or blocked to permanently prevent pregnancy, and you want to get pregnant from now on, the IVF procedure may be an alternative to tubal ligation reversal.
- Impaired sperm production or loss of sperm function: Below-average sperm count, problems with sperm movement, or abnormalities in sperm size, shape can make it difficult for sperm to fertilize an egg. If abnormalities are found in the sperm, the person may need to see a specialist to determine the underlying cause of these problems.
- Unexplained infertility: Unexplained infertility means that the cause of infertility cannot be found despite evaluation to look for common causes of infertility.
- A genetic defect: If you or your partner are at risk of passing on a genetic defect you have to your children, you may be a suitable candidate for preimplantation genetic testing, a procedure that includes IVF. After the eggs are collected and fertilized, they are screened for the presence of certain genetic problems. As a result of this screening, embryos that do not have genetic problems can be transferred to the mother's womb.
- Preservation of fertility in the presence of cancer or some other health problems: If you are going to start cancer treatments such as radiation or chemotherapy that may harm your fertility, IVF for fertility preservation may be a good option. Women can collect healthy ovaries from their ovaries and freeze them unfertilized for later use.
In cases where the uterus is not functioning properly or pregnancy poses a serious health risk to the individual, individuals may undergo IVF treatment with the help of another person (surrogate mother) to transport the embryo. In this case, the eggs taken from the mother are fertilized with sperm, but the resulting embryos are placed in the womb of the surrogate mother.

Risks of IVF Treatment
- Multiple births: If more than one embryo is transferred to your uterus during IVF treatment, you can perform multiple births (twins, triplets). A pregnancy with more than one fetus carries a higher risk of preterm birth and low birth weight than pregnancies with a single fetus.
- Premature birth and low newborn weight: Studies show that babies born after an IVF procedure slightly increase the risk of being born prematurely or being born at a low weight.
- Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome: Using injectable fertility drugs such as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) to induce ovulation can cause ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome, in which your ovaries become swollen and painful. Symptoms in this syndrome typically last for a week and include mild abdominal pain, bloating, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. But if you do become pregnant, your symptoms may last for several weeks. Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome may rarely present in a more severe form, which can also cause rapid weight gain and shortness of breath.
- Miscarriage: The rate of miscarriage in women who conceived by IVF using fresh embryos is similar to women who conceived by natural methods. This risk ratio, which is about 15% to 25%, increases with increasing maternal age.
- Complications that may occur during egg collection: The aspiration needle used to collect eggs may in some cases cause bleeding, infection or damage to the intestine, bladder, blood vessel.
- Ectopic pregnancy: About 2% to 5% of women using IVF experience an ectopic pregnancy, in which the fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in a fallopian tube. In this case, the fertilized egg cannot survive outside the uterus and there is no way to maintain the pregnancy.
- Birth defects: Maternal age is the primary risk factor for the development of birth defects, regardless of how conception was conceived. More research is needed to determine whether babies conceived using IVF are at increased risk for birth defects.
- Stress: IVF treatment can be a tiring journey financially, physically and emotionally. Support from counselors, family and friends can help you and your partner through the ups and downs of their treatment.

Preparation Before IVF Treatment in Turkey
When choosing the clinic where you will receive IVF treatment in Turkey, keep in mind that the success rate of a clinic depends on many factors, such as the patient's age and medical issues, as well as the clinic's treatment population and treatment approaches.
Before starting an IVF treatment in Turkey using your own eggs and sperm, you and your partner will likely go through a variety of tests, including:
- Ovarian reserve test: To determine the number and quality of your eggs, your doctor may test the amount of follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), estradiol (estrogen) and anti-Mullerian hormone in your blood during the first few days of your menstrual cycle. Test results, often combined with an ultrasound of your ovaries, can help predict how your ovaries will respond to fertility drugs.
- Sperm analysis: If not done as part of your initial fertility assessment, your doctor will order a semen analysis to be performed shortly before the IVF treatment cycle begins.
- Infectious disease screening: You and your partner will be screened for communicable diseases, including HIV.
- Practice (fake) embryo transfer: Your doctor may perform a mock embryo transfer to determine the depth of your uterine cavity and the technique most likely to successfully implant the embryos into your uterus.
- Uterine examination: Before starting IVF treatment, your doctor will examine the inner lining of the uterus. This examination may include sonohysterography, a technique in which a fluid is injected into your uterus through the cervix, and ultrasound imaging, which is used to create images of your uterine cavity. In addition to these, hysteroscopy with a thin, flexible, lighted device, the hysteroscope, can also be applied.
Before starting IVF treatment in Turkey, ask these questions to your doctor:
- How many embryos will be transferred with IVF treatment? : The number of embryos transferred typically depends on age and the number of eggs retrieved. Because the implantation rate is lower in older women, more embryos are usually transferred, except for women using genetically tested embryos. Most doctors follow specific guidelines to prevent multiple pregnancy (triplets or more), and in some countries legislation limits the number of embryos that can be transferred. Make sure you agree with your doctor about the number of embryos to be transferred prior to the transfer procedure.
- What did you decide to do with the extra embryos? : Extra embryos can be frozen and stored for future use for several years. Although most embryos can survive this process, not all embryos survive the freezing and thawing process. Frozen embryos make treatment cheaper and less invasive for people who decide to perform IVF again after a failed IVF treatment. On the other hand, you can donate unused frozen embryos to another couple or to a research facility. You can also choose to discard any unused embryos.
- What are your thoughts on multiple pregnancy? : If more than one embryo is transferred to your uterus, IVF treatment can result in multiple pregnancy, which poses health risks to you and your babies. In some cases, fetal reduction may be used to help a woman deliver fewer babies with fewer health risks.
- Have you thought about the decision of donor egg, sperm, embryo or surrogate mother? : A trained counselor with expertise in donor issues can help you understand concerns such as donor legal rights. You may also need the support of an attorney to file court documents to help you become the legal parents of an implanted embryo.
How IVF is Done Step by Step
IVF treatment includes several steps including stimulation of the ovaries, egg retrieval, sperm retrieval, fertilization and embryo transfer. An IVF cycle can take about two to three weeks, and multiple cycles may be required for pregnancy.
Stimulation of the Ovaries
If you are going to use your own eggs during IVF treatment, you will start treatment with synthetic hormones at the beginning of treatment to encourage the production of more than one egg instead of a single egg that normally develops each month. The presence of more than one egg is necessary as some eggs will not be fertilized during treatment or cannot develop normally after fertilization.
You may need several different medications, including:
- Medications for ovarian stimulation: An injectable medication containing follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), or a combination of both may be administered to stimulate your ovaries. These drugs encourage the development of more than one egg at the same time.
- Medications for oocyte maturation: When the follicles are ready for egg retrieval – usually after eight to 14 days – you may need to use human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG) or other medications to help the eggs mature.
- Medicines to prevent premature ovulation: These medicines prevent your body from expelling developing eggs before they develop.
- Medicines to prepare the lining of the uterus: On the day of egg retrieval or during embryo transfer, your doctor may recommend that you start taking progesterone supplements to make the lining of your uterus more susceptible to implantation.
Your doctor will create a plan with you to determine which medications to use and when to use them.
Typically, you will need one to two weeks of ovarian stimulation before your eggs are ready to be collected. To determine when the eggs are ready to be collected, your doctor will likely do the following:
- Vaginal ultrasound, in which your ovaries are imaged to monitor the development of follicles, which are fluid-filled ovarian sacs where eggs mature
- Blood tests to measure responses to ovarian stimulation drugs, such as increased estrogen as the follicles develop and progesterone levels remain low until after ovulation
In some cases, the IVF cycle needs to be canceled before egg retrieval for one of the following reasons:
- Insufficient number of developing follicles
- Early ovulation
- Increased risk of ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome as a result of the development of too many follicles
- Other medical problems
If treatment is stopped, your doctor may recommend changing medications or doses of medications to ensure a better response during future IVF treatment cycles. Or it may be concluded that you need an egg donor.
Collection of the eggs
Egg retrieval takes place 34 to 36 hours after the last injection and before ovulation.

- During the egg collection process, sedatives and pain relievers will be given.
- Transvaginal ultrasound aspiration is the most widely used method of egg retrieval. An ultrasound probe is inserted into your vagina to identify the follicles. A fine needle is then used to enter the follicles to retrieve the eggs through the vagina.
- If your ovaries are not accessible via transvaginal ultrasound, abdominal ultrasound can be used to guide the needle.
- Eggs are removed from the follicles with a needle attached to the aspiration device. More than one egg can be hatched within 20 minutes.
- You may experience cramping, bloating or a feeling of pressure after egg retrieval.
- Mature eggs are placed in a nutritious liquid (culture medium) and incubated. Eggs that appear healthy and mature will be combined with sperm to form an embryo. However, not all eggs are fertilized successfully.
Collecting Sperm
If you are going to use your partner's sperm, sperm will be collected by masturbation at the hospital on the morning of egg collection. In some cases, it may be necessary to use a needle or surgical procedure to remove sperm directly from the testis. Donor sperm can also be used. Sperm are separated from the semen in the laboratory.
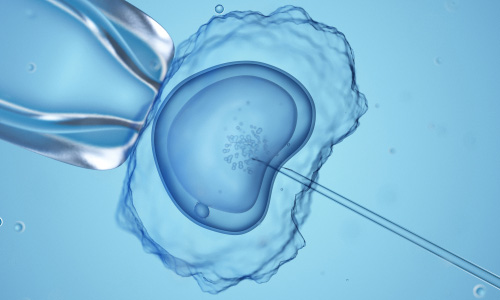
Fertilization Stage
The fertilization phase can be accomplished using two common methods:
- Conventional insemination. During the traditional fertilization process, healthy sperm and mature eggs are mixed and incubated overnight.
- Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). In ICSI, a single healthy sperm is injected directly into each mature egg. ICSI is usually performed when sperm quality or count is an issue, or when fertilization attempts have failed during previous IVF treatment cycles.
In some cases, your doctor may recommend other procedures before embryo transfer.
- Assisted hatching: About five to six days after fertilization, the embryo emerges from the surrounding membrane (zona pellucida) and implants in the inner lining of the uterus. For older women or individuals who have had multiple failed IVF attempts, your doctor may recommend this technique, in which a hole is made in the zona pellucida just before transfer to help the embryo hatch and implant. This method is also useful in the process where the egg used is a frozen egg, as freezing can harden the zona pellucida
- Preimplantation genetic testing: Embryos develop in the incubator, typically after five to six days of development, until they reach a stage where a small sample can be taken and tested for specific genetic diseases or the presence of the correct number of chromosomes. Embryos that do not contain the affected genes or chromosomes can be transferred to your uterus. While preimplantation genetic testing can reduce the likelihood that a parent will pass on a genetic problem to their baby, it cannot completely eliminate the risk.
Embryo transfer
Embryo transfer usually takes place two to five days after egg retrieval.
- A mild sedative can be used. The procedure is usually painless, but you may experience mild cramping.
- The doctor will insert a long, thin, flexible tube called a catheter into your vagina and reach your uterus through your cervix.
- A syringe containing one or more embryos suspended in a small amount of liquid is attached to the tip of the catheter.
- The doctor inserts the embryo or embryos into your uterus using the syringe.
When performed successfully, an embryo will implant in the lining of your uterus about six to 10 days after egg retrieval.
After IVF Treatment
After the embryo transfer, you can return to your normal daily activities. However, your ovaries may still be larger than normal. It is recommended that you consider avoiding vigorous activities that may cause discomfort.
Typical side effects that may be encountered after the procedure are:
- A small amount of clear or bloody fluid shortly after the procedure, due to effacement of the cervix before embryo transfer
- Sensitivity to the breast area due to high estrogen levels
- Mild swelling
- Mild cramps
- Constipation
Contact your doctor if you experience moderate or severe pain after embryo transfer. In these cases, your doctor will evaluate you for complications such as infection, ovarian twisting (ovarian torsion), and severe ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome.
Results of IVF Treatment
About 12 days to two weeks after egg retrieval, your doctor will analyze your blood sample to determine if you are pregnant.
- If you are pregnant, your doctor will refer you to an obstetrician for prenatal care.
- If you are not pregnant, you will stop using progesterone and will likely start menstruating within a week. Contact your doctor if you do not menstruate or have any unusual bleeding. If you want to try another IVF treatment cycle, your doctor can suggest steps you can take to increase your chances of conceiving through IVF.

Your ability to have a healthy pregnancy after trying IVF depends on several factors, including:
- Maternal age: The younger you are, the more likely you are to get pregnant and deliver a healthy baby using your own eggs during the IVF procedure. Women aged 41 and older are advised to consider using donor eggs during IVF to increase their chances of success.
- Embryo status: Transfer of more advanced embryos is associated with higher pregnancy rates compared to less developed embryos (embryoids on the second or third day). However, not all embryos survive the developmental process.
- Past pregnancies: Women who have given birth before are more likely to get pregnant using IVF than women who have never given birth. Success rates are lower in women who have used IVF multiple times before but did not become pregnant.
- Cause of infertility: Having normal amounts of eggs increases your chances of getting pregnant using IVF. Women with severe endometriosis are less likely to get pregnant using IVF than women with unexplained infertility.
- Lifestyle: Women who smoke usually collect fewer eggs during the IVF procedure and have a higher risk of miscarriage. Smoking can reduce a woman's chance of success in an IVF procedure by 50%. Being obese can also reduce your chances of getting pregnant and having a baby. The use of alcohol, recreational drugs, excessive caffeine, and certain drugs reduces the success rate of the IVF procedure.
IVF Treatment Costs in Turkey
There are different factors that affect the IVF treatment costs in Turkey. In some couples, some treatments may be required after fertilization is carried out before it is transferred to the expectant mother. In order for the treatments to be successful, it may even be necessary to resort to different treatments other than the tried ways.IVF treatment costs in Turkey varies based on the doctor's expertise. .

