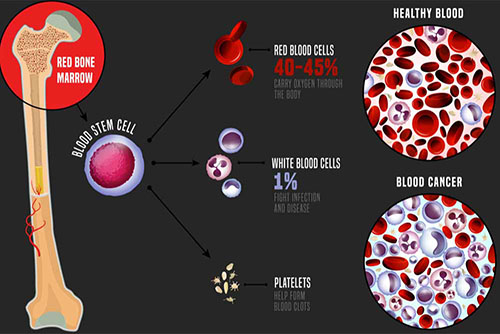
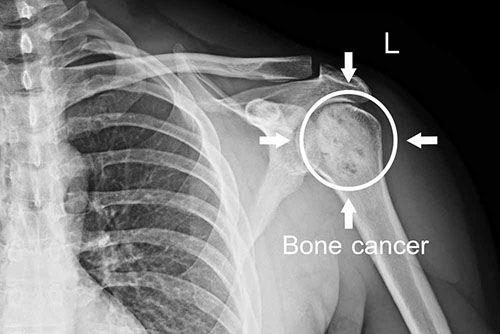
Medical Oncology
Medical oncology is a medical unit that works in coordination with branches such as surgery and radiation oncology for the diagnosis, treatment and follow-up of patients diagnosed with cancer.
A medical oncologist is an internal medicine specialist who specializes in tumor treatment.
The properties of drugs given intravenously or orally vary according to the cell type of the cancer, the organ where it started, and the area where it has spread. Medical oncology basically aims to;
- The basic expectation is to be able to heal the patient with a full cure.
- Neoadjuvant therapy to shrink the tumor and make it suitable for operation.
- Adjuvant to reduce the risk of recurrence of the disease.
- To prolong life in advanced disease
- It consists of a palliative approach to cope with both the disease and the side effects of therapeutic drugs.
Treatment Approaches in Medical Oncology
Chemotherapy
Some of the chemotherapy drugs are drugs to destroy tumor cells (cytotoxic), some are drugs that prevent the development and proliferation of the tumor by affecting the biology of the tumor (cytostatic).
Drug selection, doses and frequency of administration is evaluated by a medical oncologist according to the tumor type, prevalence, age, general condition and other existing diseases.
Nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, loss of appetite, hair loss, mouth sores, easy bruising, fever and similar conditions, which are the side effects of the drugs used, are followed up and treated by a medical oncologist.
Immunotherapy
Unlike chemotherapy, it aims to increase the body's defense against cancer with biological support instead of using chemical drugs. Immunotherapy sometimes acts on beneficial cells rather than cancer cells. In such cases, side effects of treatment occur.
Biological Therapy
Biological therapies, which are determined by identifying targets carried by cancer cells but not found in normal cells, are considered to be the most important development in cancer treatment in recent times. There are now biological agents approved by the FDA for use in many types of cancer